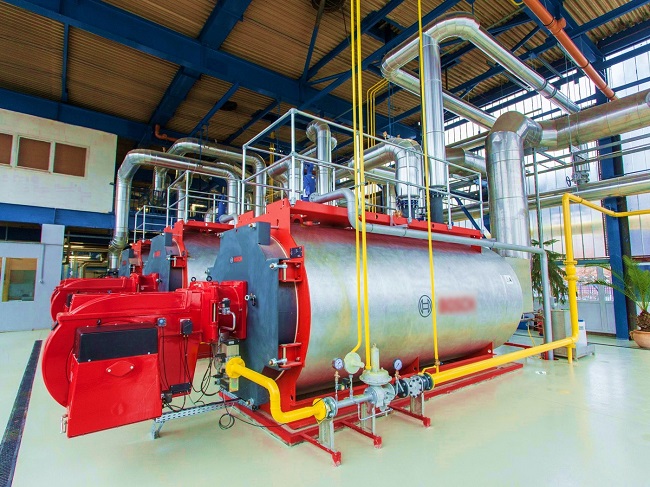

Boiler system
Boiler systems for production plants, paint lines, and oven normally include boilers, hot water piping systems, and feed pipelines. CNC-VINA is a contractor with a lot of experience in design, installation and improvement projects for production lines and paint lines for big customers in Vietnam.
The common feature of our M&E projects is to always meet: the complexity of the system, the high technical and professional requirements as well as the investor’s progress requirements. Always offering optimal solutions in design and manufacturing to save customers’ investment costs and ensure the efficiency and stable operation of the line when put into operation and use.
What is a boiler?
A steam boiler is a steam-producing heating system. It creates energy by heating water to get steam. It is a heat exchanger that makes steam for outside usage and has a combustion chamber and water container. A steam boiler burns fuel to heat water. The combination of heat and water produces steam. There are three forms of heat used to generate steam: radiation, convection, and conduction.

Types of steam boiler
Steam boilers are defined by their construction, portability, tube type, fuel type, and the pressure they produce. When boilers were initially introduced, they were as efficient as modern boilers but were dangerous since there were few control mechanisms. The size, fuel, and dimensions of a boiler change by the job it is designed to perform and the industry in which it is used. The types of fuel include electricity, wood, natural gas, coal, and fossil fuels. The difference between the fuels is their cost, eco-friendliness, and efficiency. As the demand for electricity and power generation has increased, alternative fuels have been developed.
1. Hot water boiler
Hot water boilers are tanks that transfer heat to water that is circulated for heating purposes. They are made of stainless steel, cast iron, aluminum, and steel and are capable of withstanding increased temperature and pressure.
The types of hot water boilers are defined by their tube systems, which can be fire or water. Fire tube hot water boilers have tubes immersed in water; heat moves through the tubes and heats the water around them. Water tube boilers have water inside the tubes that circulate as the tubes are heated.
2. Electric Boiler
Electric boilers use electric elements to generate heat; it is a faster and more efficient heating method. It is an eco-friendly, cleaner system since it does not necessitate the burning of fuel. Electric boilers are longer lasting, require less cleaning, and are maintenance-free. The one factor that has to be controlled with electric boilers though is the buildup of scaling in the water reservoir.
3. Gas Boiler
Gas steam boilers are powered by natural gas or propane and are more efficient than standard boilers. The fuel for a gas boiler is piped into the boiler from an outside source that is connected directly to the boiler. The distribution of heat using a gas steam boiler depends on its configuration. Gas steam boilers can be used for industrial purposes and low-pressure applications.
4. Low-pressure Boiler
Low-pressure steam boilers transfer heat at pressures between 10 and 15 psi with a temperature of 300° F (149° C). This type of boiler is used where there is little need for rapid temperature change, and where a consistent temperature is required. The popularity of low-pressure steam boilers is due to the speed at which they deliver steam; they can do so much faster than high-pressure steam boilers.
5. High-pressure Boiler
High-pressure steam boilers create excessive pressure to power equipment and machinery. The force and power of a high-pressure steam boiler are produced by a pump that forces the steam at high pressure into the circulation system. To be classified as a high-pressure steam boiler, a boiler must be able to produce pressure between 15 psi and 800 psi at temperatures that exceed 250° F (121° C).
For safety and efficiency, high-pressure steam boilers are regularly monitored for the pressure they produce and their temperature. The high-pressure loads of high-pressure steam boilers are classified as batch or continuous, with batch used for short-term demand and continuously used for long-term demand.
6. Oil Boiler
Oil steam boilers operate on the same principles as gas boilers; oil is ignited in the combustion chamber instead of gas. The burning oil heats the exchanger that heats the water. Oil steam boilers can reach an efficiency of over 90%. Though they are more expensive than gas steam boilers, they tend to have twice the lifespan of a gas boiler.
One concern with oil boilers is the need for an oil tank inside or outside that has to be refilled regularly to provide a constant supply of fuel.
7. Water Tube Boiler
Water tube boilers pass water through the tubes of the boiler. The fire created in the combustion chamber burns around the outside of the tubes and heats the tubes, thus heating the water. This boiler design produces high-pressure steam by way of the tangential pressure in the tubes, known as hoop stress; it is pressure applied to the circumference of the tubes and is like the stress applied to the bands of a wood barrel as it is filled.
Different types of water tube boilers have been used since the development of the first boiler but have gradually changed over the centuries.
The basic structure of boilers system
A steam boiler heats water much like a teapot, only on a larger and more complex scale. Though not every steam boiler is the same, there are basic elements that are common to all steam boilers: burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, expansion tank, steam temperature control, safety relief valve, and low water cutoff.
The designs and types of steam boilers widely vary depending on their construction and purpose.
1. Burner
The purpose of the burner is to inject fuel and air into the combustion area. The fuels, such as oil, gas, or pulverized coal, have to mix easily with air. Dampers are used to regulate the amount of air that enters the burner. An impeller circulates the air evenly around the burner. Pipes referred to as spuds inject the fuel into the boiler and are ignited by an igniter.
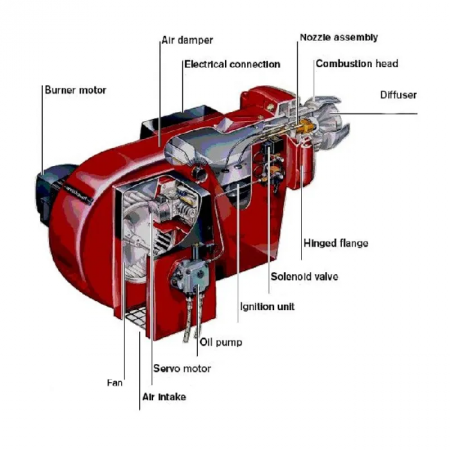
2. Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber contains the reaction of the fuel with air and uses it to create the heat to produce m. To enhance the efficiency of the combustion chamber, it needs to be adequately insulated to avoid loss of heat through radiation. The combustion chamber has tubes containing water and steam that pass through the open box with the burner and controls. Efficient combustion is an essential part of boiler operations. The heat produced in the combustion chamber is absorbed on the surface of the boiler at the top of the combustion chamber.
3. Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger allows heat to be exchanged between fluids without allowing the substances to mix. A heat exchanger contains a long coiled pipe that is immersed in the fluid to be heated. Gas or a heated liquid passes through the pipe and heats the water around it. Heat exchangers are made of a variety of materials with stainless steel being the best material since it does not corrode or rust.

4. Expansion Tank
The expansion tank helps to maintain the pressure in a boiler by providing a place for water to expand, absorb the pressure, and rate the pressure. The tank has a diaphragm that is divided into two sections with one portion accepting water from the boiler and the other side being controlled by an air valve to alleviate pressure. The air valve pushes against the water in the other section until normal pressure is reached.
5. Steam Temperature Control
Steam temperature control prevents thermal stress; precise control of steam temperature is important. The control of pressure temperature control is necessary to keep fuel costs down. Steam temperature is normally controlled by spraying water on the first and second stages superheater did using an attemperator or desuperheater.
Other methods to control steam temperature are through the use of flue gas circulation, flue gas bypass, or the tilting angle at which the burners fire the furnace. The simplest method for controlling steam temperature is to monitor the temperature of the steam as it exits the boiler and change the position of the spray water valve.
6. Safety Relief Valve
The pressure relief valve is the most important safety measure for steam boiler use. It ensures that the build-up of the pressurebuild-upeam boiler will be relieved; this assists in avoiding a catastrophic disaster. The pressure relief valve opens when the pressure reaches a critical level and closes when the pressure returns to normal.

7. Low Water Cutoff
A low water cutoff turns off the burner or shuts off fuel to a steam boiler when the water level drops below a set point. A dry fired boiler candry-firedor suffers a significant failure. Low water cutoffs are another safety feature built into a steam boiler to help avoid damage and harm to the boiler. They are a normal part of boiler construction and are installed in steam boilers and hydronic devices to shut down the boiler in the case of the loss of water.

Customers who have demand for the boiler r system please contact:
VIETNAM CNC & TECHNOLOGY APPLICATION JOINT STOCK COMPANY
North factory & Office: Song Cung Industrial Site, Dong Thap Commune, Dan Phuong District, City. Hanoi Vietnam
South office: Lot. H9, Tran Quoc Toan Str, Vo Nguyen Giap Distr., Thu Dau Mot City, Binh Duong Province
Phone: +84-915 74 4 664 / +84-915 740 880
Website: www.cncvina.com.vn; www.cncvina.net
Email: Sales01@cncvina.com.vn | Sales02@cncvina.com.vn
OUR PARTNERS














 English
English Vietnamese
Vietnamese
