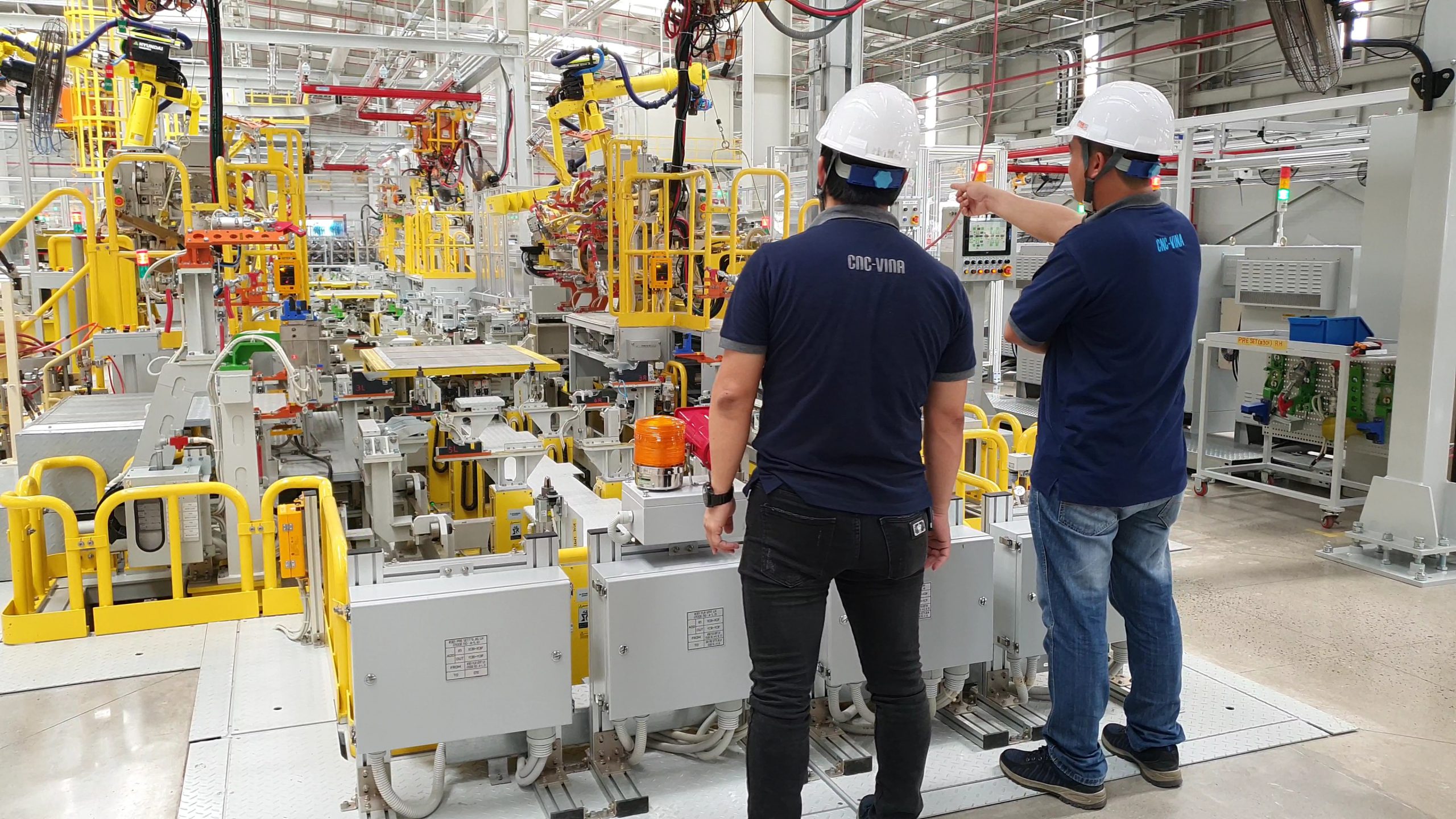

Automated welding robot installation
What is a welding robot?
A welding robot is a pre-programmed robot that helps the owner completely automate the mechanical welding process. Depending on the purpose of use, the market has produced many different types of mechanical welding robots in terms of welding heads such as welding robots, wire welding, spot welding, or laser welding...
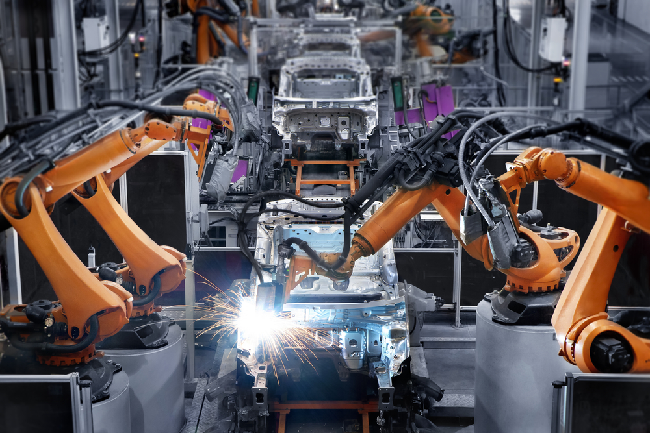
Welding robots are applied to automated production lines that require expertise and complexity such as the production of cars, motorcycles, pipes, racks, etc. Welding robots will be of great help and efficiency. superior to conventional manual labor.
Robots perform operations with high precision. First applied in the automotive industry. For nearly 50 years, the auto industry has been constantly innovating to achieve the look it is today. Car manufacturers such as Ford, Mercedes, Toyota, Honda, Nissan, etc. all apply automatic production and assembly lines, of which welding robots account for 40%. Currently, robot welding machines have developed a lot, with a variety of types: OTC welding robot, Yaskawa welding robot, Panasonic...
The advantages of robotic welding
Outstanding work efficiency: A welding robot is 5 times more likely to work than a human because the robot's welding cycle stays the same making the welding process easier and the welding performance easier to calculate. In addition, the robot is not affected by the harsh working environment.
Ability to work accurately: due to computer programming, the movements of the welding robot can achieve high accuracy and consistency, so the welding product will be the same from beginning to end. Especially for critical parts, automation gives customers confidence in the integrity of each weld.
Ensure the working environment conforms to occupational safety standards: Factors such as toxic gas, electric shock, working environment at height, unsafe, flammable, explosive, ... completely do not affect the Robot.
Solve problems related to worker skills: Welding robots work based on pre-installed programming, and businesses do not need to care about the shortage of highly qualified personnel.
Cost reduction: Robotic welding is very efficient, especially for long production runs with programming time allotted to large numbers of pieces. A modern automated welding robot can even run unattended during breaks, nights, and weekends, further reducing costs by increasing efficiency.
When to use welding robots?
A welding process involving many repetitive operations on identical parts is suitable for automation. The number of parts to be welded during the fabrication process determines whether the welding process should be automated or not. If normally it is necessary to adjust the parts to fit together or the welds are too wide or have different positions on each part, it cannot be automated.
Limitations of welding robots
Although welding robots have many advantages, they also have limitations.
Programming and training requirements: Most industrial robots require complex programming skills. So you may need to hire a new team of programmers to handle the programming of the robot. You also need specialized training and safety courses for your workers. These courses are intended to familiarize you with how to work with robots safely. Robot integrators can help you install industrial robots, or you can install them yourself with your knowledgeable staff.
Investment costs: Welding robots require a large investment – both in terms of machinery, fixtures as well as training. However, if used properly, the robot can pay for itself for one to three years. If you want to know how long you can get your investment back, you can use the Return on Investment (ROI) Calculator of robot welders online. This will tell you whether it is worth the investment or not.
Types of welding robots
This article will classify welding robots based on the welding process they use. Types of welding robots include:
Spot Welding Robot: The automotive industry often uses resistance spot welding. Spot welding robots are articulated robots. They are robots with rotating joints that range from two to 10 axes. The servo-motorized spot welding robot is equipped with a high-resolution encoder that precisely controls the movement of the spot welding gun. The welding gun has a pair of electrodes that can be opened and closed. It also comes with software that controls the robot arm's acceleration, position, and force.

Collaborative Welding Robot: Welding cobot for short, is also a robotic arm, usually 6-axis, with the torch as the end-acting part. Unlike industrial robots, cobots can work together with humans. Therefore, there is no need to place them in the welding robot chamber. You may only care about safety when soldering (flashes, sparks). They are also easy to deploy and redeploy for different tasks. With the advent of collaborative robots (or cobots), mid-sized welding businesses can also benefit from welding automation. They are also easier to program.

Shielded Metal Arc Welding Robot (SMAW): Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) is also known as rod welding. In this type of welding, an arc is created between the consumable flux electrode and the welding consumable. The SMAW robot needs to consider the change of tool center point (TCP). TCP is a variable used in robotics for the computer to track the tooltip, here the consumable electrode. The consumption rate of the electrode determines the direction of the robot arm.
Robotic Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG): Typically, robots are used for GMAW welding where high deposition rates are required to achieve high production rates. In GMAW welding, a consumable electrode is melted and acts as a filler. GMAW welding robot is used to weld stainless steel, copper, nickel, carbon steel, and aluminum. It is commonly used for metals with high electrical conductivity.

Robotic Tungsten Gas Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG): Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Robots (GTAW) is used when welding thin parts or want aesthetic and precise welds. In Robotic GTAW, variables such as torch motion, shielding gas pre-flow, pulse frequency, etc. are controlled automatically. Arc length can also be maintained automatically with automatic voltage control. The intelligent GTAW robot welding system has a camera to help monitor the joint position and detect errors. In this type of system, the operator calibrates the camera and teaches the robot to weld. The robot then takes a picture before the arc is established and compares this image with the reference image. This type of system is ideal for welding thin materials where the position of the arc plays an important factor.

Laser Welding Robot: A laser welding robot is a type of welding that uses a focused laser beam as an energy source. Robotic laser welding machine includes fiber laser head, tracking system, fiber laser, and industrial robot. It is commonly used to weld materials of different thicknesses from different angles and directions. The medical device and aerospace industries often use robotic laser welding.
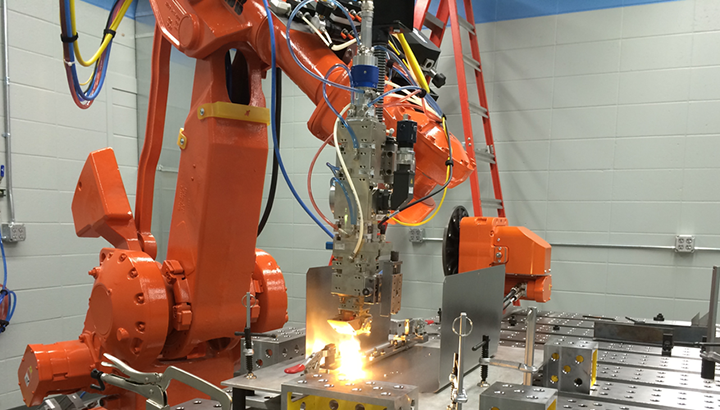
Plasma Welding Robot: This type of welding robot uses a plasma arc as a heat source to melt the junction of two metals to be welded. The plasma welding robot is equipped with a plasma torch. The electrode compresses the arc so that the plasma flows out from the torch at high speed. Plasma robots are used to weld a variety of metals regardless of their thickness. Robotic plasma welding is well known for its precise welds and short cycle times. These robots can also weld both narrow welds and welds without deforming the part.
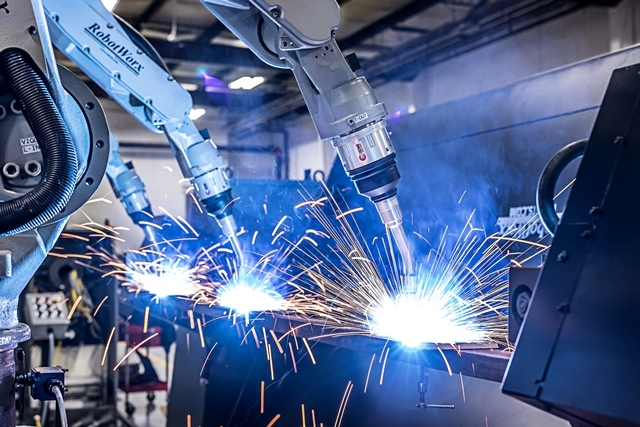

The welding industry is constantly evolving. With robotic welding and cobot welding in the industry, both small and medium welding enterprises can take advantage of robotic automation. It's an exciting time for the welding industry. With the development of technology, who knows what tomorrow's welding technology will bring?
Customers who are interested, please contact us for advice and support:
VIETNAM CNC & TECHNOLOGY APPLICATION JOINT STOCK COMPANY
North factory & Office: Song Cung Industrial Site, Dong Thap Commune, Dan Phuong District, City. Hanoi Vietnam
South office: Lot. H9, Tran Quoc Toan Str, Vo Nguyen Giap Distr., Thu Dau Mot City, Binh Duong Province
Phone: +84,915 74 4 664 / +84,915 740 880
Website: www.cncvina.com.vn; www.cncvina.net
Email: Sales01@cncvina.com.vn | Sales02@cncvina.com.vn
OUR PARTNERS














 English
English Vietnamese
Vietnamese
